Ever wonder why your doctor prescribes a certain pill and not another? The answer lies in the drug’s role—what it’s meant to treat, how it works in the body, and what side effects you might expect. Knowing the role of a medication helps you follow directions, spot red flags, and feel confident that you’re taking the right thing for your health.
If you treat a medicine like a mystery box, you risk missing doses, mixing it up with other meds, or ignoring warnings. For example, an antibiotic’s role is to kill bacteria, so stopping early can let germs survive and become resistant. A pain reliever, on the other hand, targets inflammation or nerve signals. By reading the label and understanding the purpose, you avoid common mistakes that could harm you.
Antibiotics – Fight bacterial infections. They’re useless against viruses, so they shouldn’t be used for colds.
Antihistamines – Block histamine to reduce allergy symptoms like sneezing and itching.
Blood pressure meds – Lower heart strain by relaxing vessels or slowing the heart.
These are just a few examples, but each class has a clear job that guides dosage, timing, and safety tips.
When you pick up a prescription, look for three clues: the drug name, its main use (often listed under "Indications"), and any special instructions. If the label says “Take with food,” that’s because the medication’s role involves slow absorption to avoid stomach irritation.
Over‑the‑counter products follow the same rule. A supplement labeled as a “probiotic” aims to balance gut bacteria, while a “vitamin D tablet” supports bone health. Even though you don’t need a prescription, knowing why you’re taking it prevents waste and side effects.
If you ever feel unsure, ask yourself three quick questions: What problem is this drug solving? How does it work—by killing germs, reducing inflammation, or changing hormone levels? What should I watch out for while using it?
Answering these helps you spot mismatches. For instance, taking a diuretic (a water‑pill) without needing it can cause dehydration, while mixing a blood thinner with certain painkillers raises bleeding risk.
Keep a simple cheat sheet in your phone or on the fridge: drug name, purpose, dose, and any no‑go combos. Updating it whenever you start a new prescription saves time at the pharmacy and keeps doctors in the loop during appointments.
Remember, the role of a medication isn’t set in stone—doctors may adjust it based on your response or other health changes. Regular check‑ins let them fine‑tune treatment so you stay on track without unwanted side effects.
Bottom line: Understanding what each drug is designed to do empowers you to use it safely, get the best results, and avoid costly mistakes. Next time you open a pill bottle, take a quick look at its role—you’ll thank yourself later.

As a blogger, I've come across a crucial topic in managing heart failure - the role of Atenolol-Chlorthalidone. This combination of medications is known to effectively treat high blood pressure, which is a significant risk factor for heart failure. Atenolol, a beta-blocker, helps in reducing the heart rate and blood pressure, while Chlorthalidone, a diuretic, aids in eliminating excess fluid from the body. Together, they work to reduce the workload on the heart, ultimately improving its function and decreasing the risk of heart failure. It's essential to consult with your doctor for proper dosage and prescription to ensure the best possible outcome in managing heart failure.
As a blogger, I've recently delved into the role of surgery in treating Graves' disease. Surgery, specifically thyroidectomy, is one of the three primary treatment options for this condition, alongside medication and radioactive iodine therapy. It involves removing all or part of the thyroid gland, which can provide long-term relief from symptoms. Although it may not be the first choice for many patients, surgery can be especially beneficial for those with large goiters, pregnant women, or individuals who cannot tolerate other treatments. Overall, surgery plays a crucial role in Graves' disease treatment and can offer life-changing results for patients in specific circumstances.
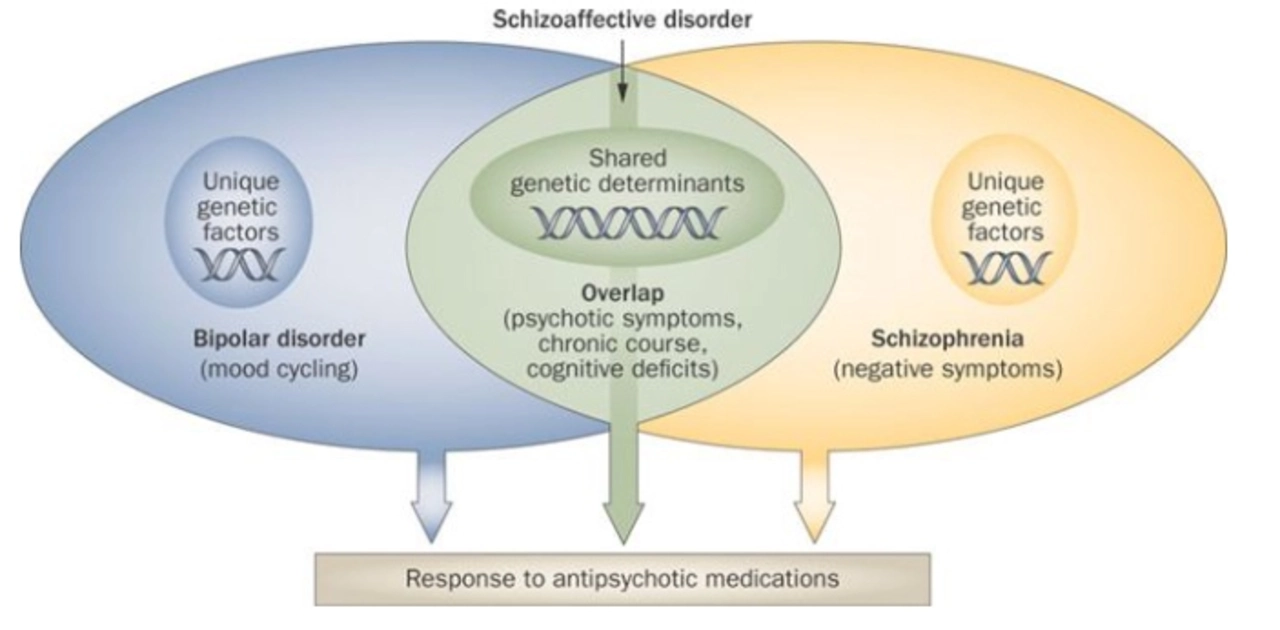
As a blogger, I've recently come across the topic of the role of Clozapine in the management of psychotic depression. Clozapine, an atypical antipsychotic medication, is used to treat severe cases of this mental health disorder when other treatments have failed. Its unique properties help in alleviating both psychotic symptoms and depressive episodes. However, it's essential to be aware of the potential side effects and monitor blood levels closely while administering this medication. In conclusion, Clozapine plays a crucial role in managing psychotic depression, improving the quality of life for those who suffer from this challenging condition.
Debunking common medication safety myths with facts backed by CDC, FDA, and pharmacy data to help patients avoid dangerous errors and take their meds safely.
In 2025, the landscape of hypothyroidism treatment offers a range of alternatives to Synthroid. These options cater to diverse patient needs, from synthetic solutions to natural remedies. This article delves into ten compelling alternatives, examining their benefits and drawbacks. With personalized medicine gaining momentum, understanding these options empowers patients to make informed choices in collaboration with their healthcare providers.
The FDA's black box warning on antidepressants warns of increased suicidal thoughts in young people - but the real danger may be avoiding treatment altogether. Here's what the data really shows.
Learn where to find trusted online pharmacies, compare prices, verify legitimacy, and safely purchase cheap generic clindamycin with step‑by‑step guidance.
I recently came across the topic of osteodystrophy and its effects on dental health, which I found quite intriguing. Osteodystrophy is a condition that affects bone metabolism and can have a significant impact on our teeth and gums. It is important for us to understand the link between these two aspects of our health, as it can help us take better care of our oral hygiene. In my research, I discovered that proper dental care and regular check-ups are crucial in managing this condition. I'll be sharing more information on this topic in my upcoming blog post, so stay tuned!