When your blood has too much hyperkalemia, a condition where potassium levels in the blood rise above normal limits, often without clear symptoms until it becomes dangerous. Also known as high potassium, it’s not just a lab number—it’s a real risk to your heart. Most people don’t feel anything until their heartbeat goes off rhythm, which can lead to cardiac arrest. That’s why it’s called a silent threat—especially if you’re on medications for high blood pressure, heart failure, or kidney disease.
ACE inhibitors, a common class of blood pressure drugs including lisinopril and enalapril are one of the top causes. They help your kidneys filter better, but that same effect can cause potassium to build up. Same goes for ARBs, like losartan and valsartan, and potassium-sparing diuretics, such as spironolactone and eplerenone. These are lifesavers for many, but they’re also the reason your doctor checks your potassium levels every few months. Even salt substitutes with potassium chloride can push levels over the edge if you’re already on these meds.
People with kidney disease, especially those in later stages are at the highest risk. Your kidneys are the main way your body gets rid of extra potassium. When they’re not working well, potassium sticks around. That’s why so many posts on this site talk about drug interactions, generic switches, and medication safety—because even small changes in your routine can trigger a spike. A new generic version of your blood pressure pill, skipping a dose of a diuretic, or even eating too many bananas or spinach in one day can matter more than you think.
It’s not just about avoiding potassium-rich foods. It’s about understanding how your meds work together. If you’re on a beta-blocker with an ACE inhibitor, or taking NSAIDs like ibuprofen on top of your kidney meds, you’re stacking risks. Many patients don’t realize their pharmacist can spot these hidden dangers during a medication review. That’s why posts on pharmacy consultations, drug interactions, and generic switching are so relevant here—they’re not just about cost, they’re about survival.
You don’t need to live in fear. But you do need to be aware. Regular blood tests, clear communication with your doctor, and knowing which meds to double-check with your pharmacist can keep you safe. The posts below cover exactly these kinds of real-world situations—how drugs interact, how generics can change your risk, and how to protect yourself when you’re managing multiple conditions. What you’ll find here isn’t theory. It’s what actually keeps people out of the ER.
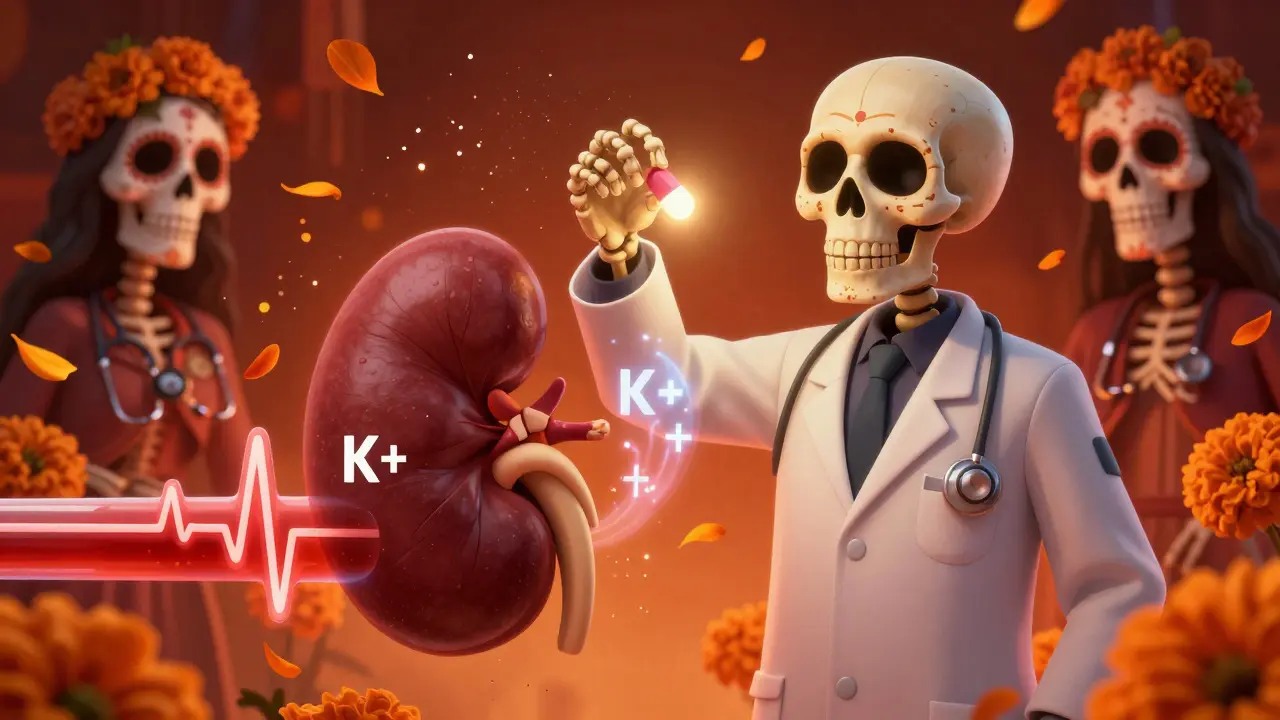
Trimethoprim, found in Bactrim and Septra, can cause dangerous spikes in potassium levels, especially in older adults and those on blood pressure meds. Learn who’s at risk, how fast it happens, and what to ask your doctor.
Hello there! In today's post, we're discussing a vital topic, which is the role of Alfacalcidol in preventing Rickets in children. It's crucial for us, as parents, to understand what exactly Alfacalcidol is and how it plays an integral role in strengthening our children's health. I'll be providing information about this amazing form of Vitamin D and highlighting how its timely administration can contribute significantly towards the prevention of rickets. Stay tuned for an insightful read!
Cut through the confusion of online Tofranil shopping. Here’s what you really need to know to buy antidepressants online, stay safe, and avoid scams.
Authorized generics are identical to brand-name drugs but cost less because they skip marketing costs and trigger immediate price competition. Learn how they work, why they’re cheaper, and how to get them.
Benzodiazepines pose serious risks for seniors including falls, memory loss, and dementia. Safer alternatives like CBT-I, SSRIs, and ramelteon offer effective, long-term relief without the dangers. Learn why experts now recommend avoiding these drugs and how to transition safely.
Learn safe ways to purchase cheap generic Singulair online, compare prices, verify pharmacies, and save on your asthma medication.