When you hear generic drugs, lower-cost versions of brand-name medications that contain the same active ingredients and meet the same safety standards. Also known as generic medications, they make up over 90% of prescriptions filled in the U.S. and help millions afford life-saving treatments every year. But not all generics are created equal—and knowing the difference can save you money, avoid side effects, or even prevent a dangerous reaction.
Many people assume a generic is just a cheaper copy, but that’s not the whole story. The FDA requires generics to have the same active ingredient, strength, dosage form, and route of administration as the brand name. That means generic drugs work the same way in your body. But here’s what most don’t tell you: the inactive ingredients—like fillers, dyes, and preservatives—can be completely different. That’s why some people report side effects when switching from brand to generic, even if their doctor says it’s "the same drug." These differences matter if you’re allergic to lactose, gluten, or certain dyes. That’s where authorized generics, exact copies of brand-name drugs made by the same company under a different label come in. They’re not just cheaper—they’re often identical in every way, down to the inactive ingredients.
Then there’s the money. When a brand-name drug’s patent expires, other companies can make the same drug. The first generic usually cuts the price by 30-50%. But when a second or third company enters the market? Prices can drop by 80% or more. That’s how a $300 monthly pill becomes a $20 one. And it’s not just for expensive drugs—insulin, blood pressure meds, and antidepressants all follow this pattern. But here’s the catch: sometimes, even with multiple generics available, prices stay high because of supply chain issues, lack of competition, or pharmacy benefit managers locking out cheaper options. That’s why knowing how to ask for the lowest-cost generic—or even an authorized version—can make a real difference in your wallet.
And it’s not just about cost. Some people switch to generics and feel worse—not because the drug doesn’t work, but because their body reacts to a new filler. That’s why checking the inactive ingredients matters. If you’ve ever had an unexpected reaction after switching pills, it might not be the drug—it’s the stuff holding it together. That’s why posts here dig into everything from how to read a pill’s label to why some pharmacies quietly swap generics without telling you.
What you’ll find below isn’t just theory. It’s real-world advice from people who’ve been there: how to avoid hidden costs, how to spot when a generic isn’t right for you, why authorized generics sometimes beat regular ones, and what to say to your pharmacist when something feels off. Whether you’re managing diabetes, high blood pressure, or depression, understanding generics isn’t just smart—it’s essential.

Generic substitution in workers' compensation saves billions by replacing brand-name drugs with equally effective generics. Learn how it works, when it’s required, and what injured workers should know.
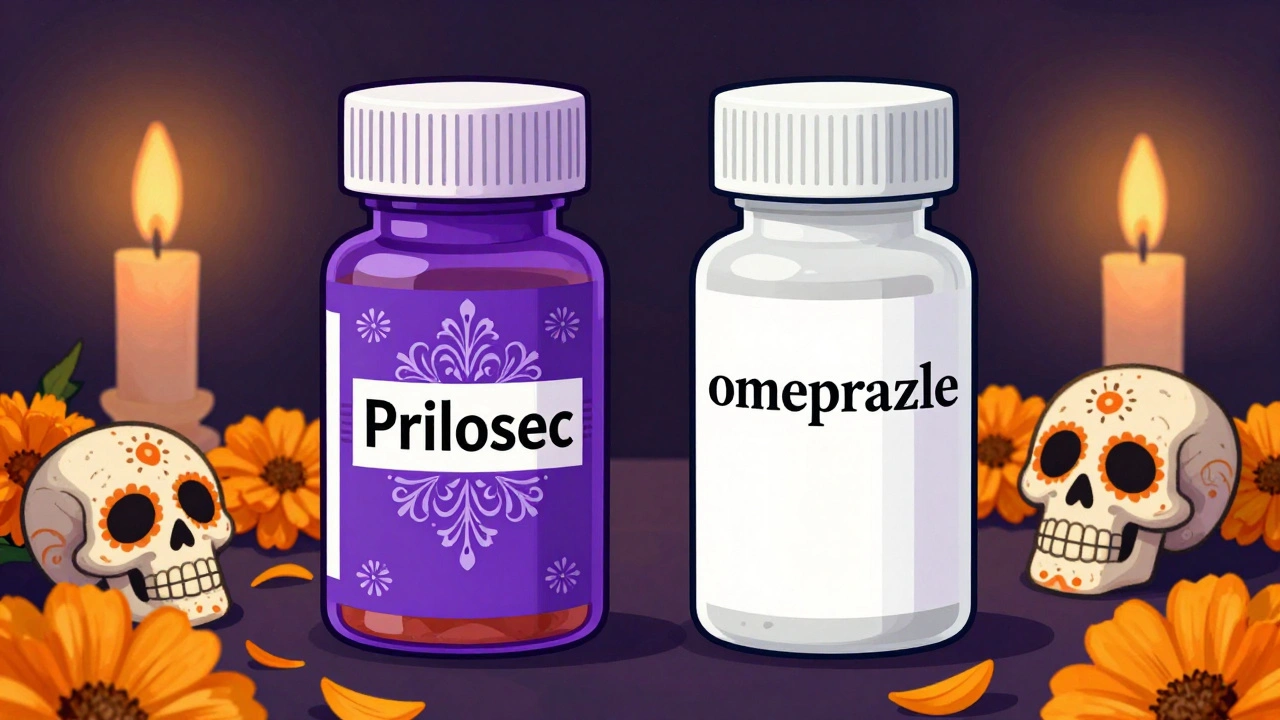
Generic drugs save billions and work just as well as brand-name versions. Learn what the FDA requires for therapeutic equivalence, why labels look different, and when to watch for subtle changes.
Learn how to set up and safely use an insulin pump for diabetes management. Understand basal rates, bolus types, site care, and real-world safety tips to avoid dangerous complications.
Neurontin (Gabapentin) is commonly used for epilepsy and nerve pain, but it’s not the only option out there. This article explores eight different alternatives available in 2025, weighing their benefits and downsides. Whether you’re seeking different epilepsy treatments or exploring options for bipolar disorder, this guide will help you navigate your choices. Each option is described with practical pros and cons to help you make an informed decision.
Explore how antioxidant supplements can reduce oxidative stress, ease pain, and support standard therapy for chronic pancreatitis, with dosing tips and safety advice.
Curious about mixing spironolactone and alcohol in 2024? This article breaks down new clinical research on hormone levels and liver effects when the two are combined. Packed with facts, stats, and relatable situations, you'll find smart tips and an honest look at what doctors and studies really say. Readers will understand potential risks, latest findings, and safer habits for daily life—all in plain language.
A detailed side‑by‑side look at Periactin (Cyproheptadine) versus other antihistamines, covering uses, dosing, side effects, and how to pick the best option for you.