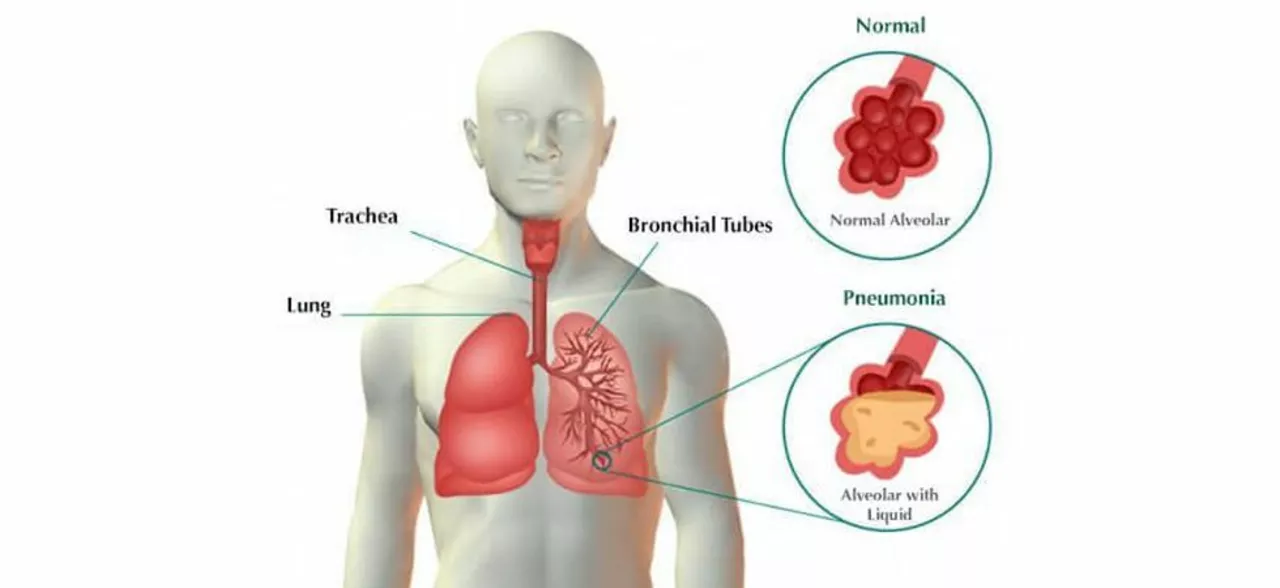
Understanding the Connection Between Pneumonia and Diabetes
As a person living with diabetes, it is essential to be aware of the potential complications that can arise from this condition. One such complication is an increased risk of developing pneumonia. In this article, I will explore the connection between pneumonia and diabetes and share some crucial information that can help you better manage your health.
The Increased Risk of Pneumonia in Diabetics
People with diabetes are at a greater risk of developing pneumonia due to a weakened immune system. High blood sugar levels can impair the body's ability to fight off infections, leaving diabetics more susceptible to illnesses like pneumonia. Additionally, diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels, which can lead to reduced blood flow and oxygen supply to the lungs, further increasing the risk of pneumonia.
Studies have shown that people with diabetes are three times more likely to be hospitalized for pneumonia than those without diabetes. Furthermore, diabetics who develop pneumonia often have a longer hospital stay and a higher risk of complications compared to non-diabetics.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Pneumonia
Early detection and treatment of pneumonia are crucial, especially for people with diabetes. Here are some common symptoms of pneumonia that you should be aware of:
- Cough with phlegm or mucus
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain when breathing or coughing
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult your healthcare provider immediately for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Preventing Pneumonia: Vaccination and Lifestyle Choices
One of the most effective ways to prevent pneumonia in people with diabetes is through vaccination. There are two types of vaccines available to protect against pneumonia: the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13) and the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23). Your healthcare provider can help determine which vaccine is appropriate for you and when you should receive it.
Aside from vaccination, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial in preventing pneumonia. Some steps you can take include:
- Managing your blood sugar levels
- Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke
- Exercising regularly
- Eating a well-balanced diet
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently
Treating Pneumonia in Diabetics
If you are diagnosed with pneumonia, it is crucial to follow your healthcare provider's recommendations for treatment. This may include taking prescribed antibiotics, getting plenty of rest, and staying hydrated. Additionally, it is essential to monitor and manage your blood sugar levels closely during this time, as illness can cause fluctuations in blood sugar.
In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary for people with diabetes who develop pneumonia. This is especially true if your blood sugar levels are difficult to control or if you have other complications, such as kidney or heart problems.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels During Illness
As mentioned earlier, illness can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, making it even more crucial for people with diabetes to monitor their levels closely during this time. Here are some tips for managing your blood sugar during illness:
- Check your blood sugar levels more frequently than usual
- Continue taking your diabetes medication as prescribed, even if you have a reduced appetite
- Stay hydrated by drinking water, sugar-free beverages, or broth
- Contact your healthcare provider if your blood sugar levels remain consistently high or low
Conclusion
Pneumonia is a serious health concern for people with diabetes, but with proper knowledge and proactive measures, you can reduce your risk and manage your health effectively. By understanding the connection between pneumonia and diabetes, recognizing the symptoms, staying up-to-date on vaccinations, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you can take steps to protect yourself and live a healthier life with diabetes.