Understanding Atrophic Gastroenteritis and Its Causes
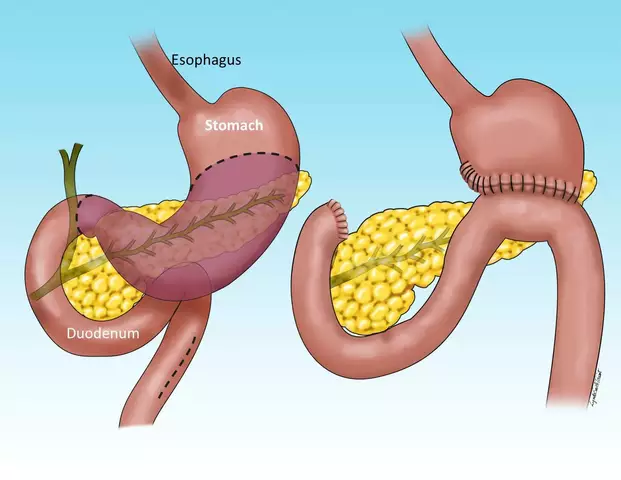
Atrophic gastroenteritis is a medical condition characterized by chronic inflammation and thinning of the stomach lining. It is caused by a variety of factors, including bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, and long-term use of certain medications. In this section, we will delve into the causes of atrophic gastroenteritis, focusing on the most common culprit: the Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria. We will also discuss other possible factors that may contribute to the development of this condition, such as autoimmune gastritis and certain medications.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Atrophic Gastroenteritis
Many people with atrophic gastroenteritis may not experience any symptoms, making it difficult to detect and diagnose. However, some individuals may develop various signs and symptoms that can point to this condition. In this section, we will discuss the most common symptoms of atrophic gastroenteritis, such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss. We will also explore the potential complications that may arise from this condition, including anemia and vitamin B12 deficiency.
How Atrophic Gastroenteritis Increases Gastric Cancer Risk
Atrophic gastroenteritis is a significant risk factor for the development of gastric cancer. The chronic inflammation and thinning of the stomach lining can lead to the formation of precancerous lesions and, eventually, cancerous cells. In this section, we will explore the connection between atrophic gastroenteritis and gastric cancer, highlighting the role of H. pylori infection in this process. We will also discuss other factors that may increase one's risk of developing gastric cancer, such as age, gender, and dietary habits.
Diagnosis and Staging of Atrophic Gastroenteritis
Diagnosing atrophic gastroenteritis can be challenging due to the lack of specific symptoms. However, several diagnostic tests can help identify this condition, such as blood tests, endoscopy, and biopsy. In this section, we will discuss the various diagnostic tools available for detecting atrophic gastroenteritis and how they can help determine the severity of the condition. We will also explore the different stages of atrophic gastroenteritis, ranging from mild to severe, and how they relate to one's risk of developing gastric cancer.
Treatment Options for Atrophic Gastroenteritis
Treating atrophic gastroenteritis depends on the underlying cause of the condition. For example, if H. pylori infection is the main cause, a combination of antibiotics and acid-suppressing medications may be prescribed. In this section, we will discuss the various treatment options available for managing atrophic gastroenteritis, including medications, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications. We will also explore the role of regular monitoring and follow-up care in preventing the progression of this condition and reducing the risk of gastric cancer.
Preventing Gastric Cancer in Atrophic Gastroenteritis Patients
Preventing gastric cancer is of utmost importance for individuals with atrophic gastroenteritis, as they are at a higher risk of developing this deadly disease. In this section, we will discuss various strategies for reducing one's risk of gastric cancer, such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding certain environmental factors. We will also explore the role of screening and surveillance in detecting precancerous lesions and early-stage gastric cancer, allowing for prompt treatment and improved outcomes.
Living with Atrophic Gastroenteritis: Tips for Managing Symptoms and Improving Quality of Life
Living with atrophic gastroenteritis can be challenging, as it may cause discomfort and disrupt daily activities. However, by implementing certain lifestyle changes and adhering to a prescribed treatment plan, patients can effectively manage their symptoms and reduce their risk of developing gastric cancer. In this section, we will share some practical tips for living with atrophic gastroenteritis, such as dietary modifications, stress management techniques, and support resources. We will also discuss the importance of maintaining a positive outlook and staying proactive in one's healthcare journey.