If you take prescription or over‑the‑counter drugs, you might wonder how a workout will affect them. The short answer is that exercise can speed up, slow down, or even change the way a medication works in your body. Knowing the basics helps you avoid surprises at the gym and stay healthy.
First, understand that many medicines are processed by the liver and kidneys. When you push yourself physically, blood flow to these organs shifts, which can alter drug metabolism. For some drugs, this means they clear faster and lose effectiveness; for others, they linger longer and increase side‑effects.
Blood pressure meds: Running or lifting weights can drop your blood pressure temporarily. If you’re on antihypertensives like lisinopril, you might feel dizzy or light‑headed after a hard set. Keep the intensity moderate until you know how your body reacts.
Blood thinners: Drugs such as warfarin thin your blood to prevent clots. Strenuous activity can cause tiny injuries that bleed longer than usual. If you notice bruises or prolonged bleeding, talk to your doctor about adjusting the dose.
Stimulants and ADHD meds: Medications like Adderall raise heart rate and energy. Adding a high‑intensity cardio session can push those numbers too high, leading to palpitations or anxiety. A lighter workout or timing your dose away from exercise may help.
Diabetes drugs: Insulin and oral agents lower blood sugar. Exercise also drops glucose levels, so you risk hypoglycemia if you don’t adjust food intake or medication timing. Keep a quick snack handy and monitor your meter before, during, and after the session.
Start slow. If you’re new to exercise or have just begun a new prescription, ease into it with short walks or light resistance training. This lets you see how your body reacts without overloading any system.
Stay hydrated. Dehydration can magnify side‑effects like dizziness or low blood pressure. Aim for at least eight ounces of water every 20 minutes during moderate activity.
Track timing. Many experts suggest taking meds that lower blood pressure in the morning and exercising later in the day, when your body has already absorbed the dose. For diabetes drugs, a short snack before exercise can prevent lows.
Listen to your body. If you feel unusual fatigue, chest pain, or excessive shortness of breath, stop and rest. These signals often mean the drug‑exercise combo isn’t sitting right.
Ask your pharmacist or doctor. They can tell you if a specific drug needs dose tweaks when you’re active. A quick call before starting a new program can save you from uncomfortable side‑effects.
Remember, staying active is good for most health conditions, but the key is balance. With a little planning, you can keep your workouts effective and your medication working as intended.
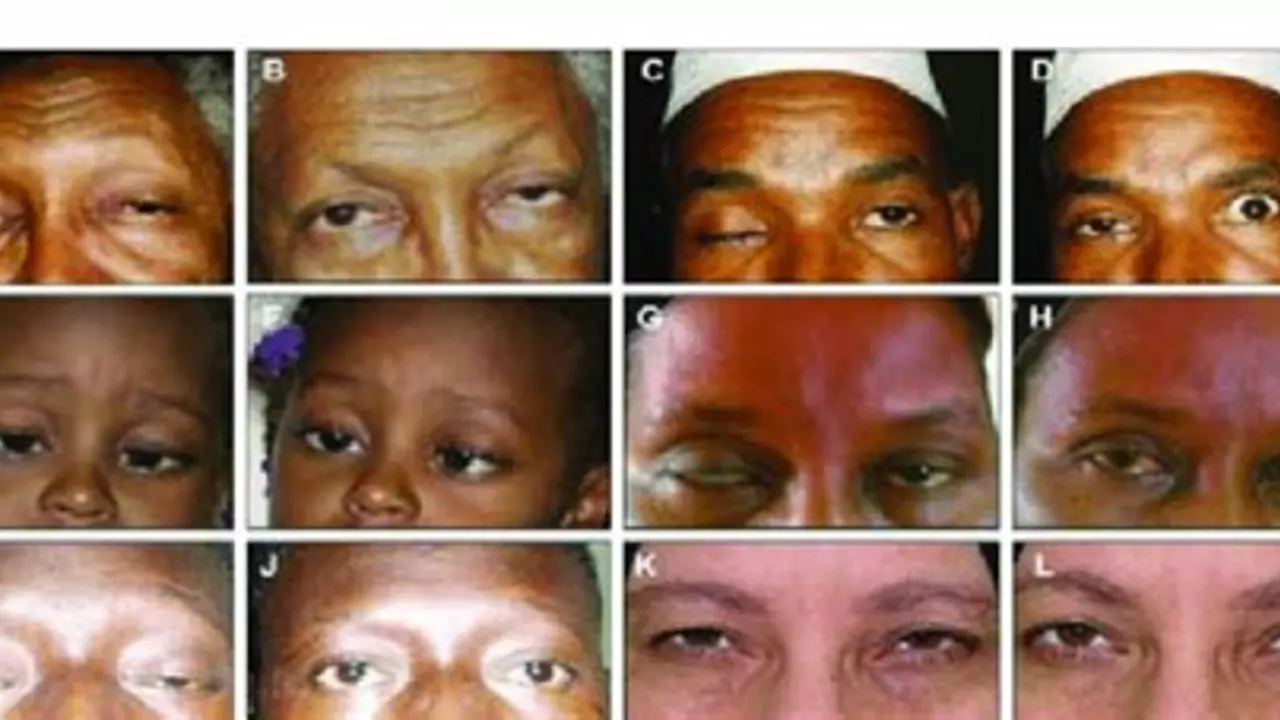
In my recent post, I discussed the relationship between Pyridostigmine Bromide and exercise for those living with Myasthenia Gravis. I explored how this medication can improve muscle strength, making physical activity more manageable for patients. However, I also highlighted the importance of balancing exercise with rest periods and working closely with healthcare providers to establish a suitable routine. Furthermore, it's crucial to listen to your body and not push too hard, as overexertion can lead to symptom flare-ups. Overall, while Pyridostigmine Bromide can aid in physical activity, careful management is key.
Actinic keratoses are precancerous skin patches caused by sun damage. Learn how field treatments like topical creams and photodynamic therapy can prevent them from turning into skin cancer.
Secondary patents let pharmaceutical companies extend market exclusivity by patenting minor changes to drugs - not the active ingredient, but how it's delivered, used, or made. These tactics delay generics and keep prices high.
SGLT2 inhibitors like Jardiance and Farxiga lower blood sugar while protecting the heart and kidneys. Learn how they work, who benefits most, and what side effects to watch for.
Explore how lurasidone impacts cognition in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, reviewing clinical trials, mechanisms, and practical guidance for clinicians.
Learn the critical difference between serious and non-serious adverse events in clinical trials-and when each must be reported. Understand the six FDA criteria, avoid common mistakes, and ensure patient safety without overwhelming the system.